 Pelvic Tilt - Into Bridge
Pelvic Tilt - Into Bridge
Benefits: This exercise will also work the abs and glutes.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the lower back muscles.
Intermediate Lower Back Abdominals Glutes Stretching Body Only Gym Home
General Info: The muscles of the lower back straighten the spine. They work together with the abdominals to keep the spine upright. The spine plays a big role in overall health, so the lower back is one of the most important muscle groups in the body.
 Pike - Hanging
Pike - Hanging
Benefits: This exercise is a great way to fine tune your abdominals. A hanging ab exercise like this one also removes an lower back stress.
Purpose: This exercise works the abdominals.
Beginner Abdominals Strength Body Only Pull Gym
General Info: The abdominals consist of the abs and the obliques. The abs can be divided into upper abs and lower abs. The upper abs are involved in work done with the lower abs and with twisting movements (obliques).
 Plank - Fitness Ball
Plank - Fitness Ball
Benefits: This exercise will assist in giving you strong abdominals. This exercise looks easy but is very beneficial for the abdominal muscles.
Purpose: This exercise provides flexibility and mobility of the hamstrings.
Beginner Abdominals Hip Flexors Strength Fitness Ball Gym
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
 Plank - Fitness Ball Reverse
Plank - Fitness Ball Reverse
Benefits: This exercise will assist in giving you strong abdominals.
Purpose: This exercise provides flexibility and mobility of the hamstrings.
Beginner Abdominals Hip Flexors Strength Fitness Ball Gym
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
 Plate Curl - Fitness Ball
Plate Curl - Fitness Ball
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Plate Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
 Plate Curl - Reverse
Plate Curl - Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Plate Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
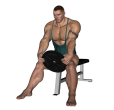 Plate Curl - Seated
Plate Curl - Seated
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Plate Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
 Plate Curl - Seated Reverse
Plate Curl - Seated Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Plate Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
 Plate Curl - Squat
Plate Curl - Squat
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Intermediate Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Plate Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
 Plate Curl - Standing
Plate Curl - Standing
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Plate Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand..
 Plate Curl - Standing Incline
Plate Curl - Standing Incline
Benefits: This exercise works both heads of the biceps and is very similar to the preacher curl.
Purpose: This exercise is used to target the biceps muscle to develop size, definition, strength, endurance and power.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Strength Plate Incline Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joint. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Plate Pinch - Basic
Plate Pinch - Basic
Benefits: This exercise focuses finger gripping and strength. To get the greatest benefit from this exercise, ensure that you hold the plates until you cannot hold them any longer, then minimum rest and do it again.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the forearm muscles as well as finger strength.
Intermediate Forearms Fingers Strength Plate Gym
General Info: A complete forearm program must achieve balanced development for all major forearm muscles. The forearm is involved in six different forearm movements. They include wrist flexion, wrist extension, wrist abduction, wrist adduction, forearm pronation, and forearm supination. There are additional muscles found in the forearm that are involved in movements like elbow flexion (brachioradialis), finger flexion, and finger extension.
 Plate Pull - Seated Bent Over
Plate Pull - Seated Bent Over
Benefits: This exercise has a different resistance curve from back extensions so these two exercises make a good combination.
Purpose: This exercise can be a powerful tool for developing the spinal erectors.
Intermediate Lower Back Hamstrings Glutes Strength Plate Flat Bench Push Compound Gym
General Info: The muscles of the lower back straighten the spine. They work together with the abdominals to keep the spine upright. Good Mornings places a lot of stress on the lower back.
 Posterior Raise - Basic
Posterior Raise - Basic
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Bottle Head On Chair
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Bottle Head On Chair
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Water Bottle Chair Pull Home
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Head On Bench
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Head On Bench
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Narrow Stance
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Narrow Stance
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Wide Stance
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Dumbbell Wide Stance
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Seated
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Seated
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Seated Water Bottle
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Seated Water Bottle
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Water Bottle Chair Pull Home
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Water Bottle Pull Compound Home
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle Narrow
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle Narrow
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Water Bottle Pull Compound Home
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle Wide
Posterior Raise - Bent Over Water Bottle Wide
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Water Bottle Pull Compound Home
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Cable Rope
Posterior Raise - Cable Rope
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength High Low Cable Machine Cable Rope Attachment Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Dumbbell Incline
Posterior Raise - Dumbbell Incline
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Face Down Barbell Close Grip
Posterior Raise - Face Down Barbell Close Grip
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle as well as the anterior delt muscle
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the front and rear deltoid muscle areas.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Front Shoulders Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Face Down Barbell Straight Grip
Posterior Raise - Face Down Barbell Straight Grip
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle as well as the anterior delt muscle
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the front and rear deltoid muscle areas.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Front Shoulders Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Face Down Dumbbell
Posterior Raise - Face Down Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Fitness Ball Dumbbell
Posterior Raise - Fitness Ball Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Flat Bench Dumbbell
Posterior Raise - Flat Bench Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Flat Bench Dumbbell Reverse
Posterior Raise - Flat Bench Dumbbell Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Flat Dumbbell Alternate
Posterior Raise - Flat Dumbbell Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Flat Dumbbell Feet Up
Posterior Raise - Flat Dumbbell Feet Up
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Incline Dumbbell
Posterior Raise - Incline Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Incline Dumbbell Feet Up
Posterior Raise - Incline Dumbbell Feet Up
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Low Pulley Single
Posterior Raise - Low Pulley Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Traps Strength High Low Cable Machine Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Lying
Posterior Raise - Lying
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Pec Dec Machine
Posterior Raise - Pec Dec Machine
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Triceps Strength Pec Dec Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Resistance Tube Bent Over
Posterior Raise - Resistance Tube Bent Over
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Beginner Rear Shoulders Biceps Lats Traps Strength Resistance Tube Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Standing With Band
Posterior Raise - Standing With Band
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Triceps Strength Band Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Posterior Raise - Twin Pulley
Posterior Raise - Twin Pulley
Benefits: This exercise isolates the posterior delt muscle.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the rear deltoid muscle area.
Intermediate Rear Shoulders Lats Traps Triceps Strength High Low Cable Machine Pull Gym
General Info: The posterior (rear) deltoid or shoulder is one of the three distinct heads of the deltoid anatomy. It is typically used in tandem with the back muscles during upper body pulling exercises.
 Preacher Curl - Ball Dumbbell Hammer Single
Preacher Curl - Ball Dumbbell Hammer Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Ball Dumbbell Zottman Single
Preacher Curl - Ball Dumbbell Zottman Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Barbell
Preacher Curl - Barbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Barbell Reverse
Preacher Curl - Barbell Reverse
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Barbell Reverse Close Grip
Preacher Curl - Barbell Reverse Close Grip
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Barbell With Chains
Preacher Curl - Barbell With Chains
Benefits: This exercise is done with the addition of chains. The primary function of chains is to accommodate resistance. Chains are also a great means of weight loading (adding more weight to an exercise). Chains are also a great way for working the stabilizers.
Purpose: Benefits This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Chains Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Basic
Preacher Curl - Basic
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Cable
Preacher Curl - Cable
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The cable keeps tension on the muscles throughout the exercise.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Cable Machine Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Alternate
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Hammer
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Hammer
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse Alternate
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse Alternate
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse Single
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Reverse Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Single
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Alternate
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Reverse
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Reverse Alternate
Preacher Curl - Dumbbell Zottman Reverse Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - EZ Bar
Preacher Curl - EZ Bar
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - EZ Bar Reverse
Preacher Curl - EZ Bar Reverse
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength EZ Bar Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - EZ Bar Reverse Close Grip
Preacher Curl - EZ Bar Reverse Close Grip
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength EZ Bar Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Fit Ball Dumbbell Reverse Single
Preacher Curl - Fit Ball Dumbbell Reverse Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Close Grip
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Close Grip
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Hammer
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Hammer
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Hammer Barbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Reverse
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Reverse Close
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Barbell Reverse Close
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Barbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Alternate
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Hammer
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Hammer
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Hammer Alternate
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Hammer Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Reverse
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Reverse
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Reverse Alternate
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Reverse Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Single
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Single
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Zottman
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Zottman
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Zottman Alternate
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball Dumbbell Zottman Alternate
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength EZ Bar Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Close Grip
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Close Grip
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength EZ Bar Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Reverse Close
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Reverse Close
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength EZ Bar Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Wide Grip
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Bar Wide Grip
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength EZ Bar Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Reverse
Preacher Curl - Fitness Ball EZ Reverse
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls. The reverse grip makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength EZ Bar Fitness Ball Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Hammer Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Hammer Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Machine
Preacher Curl - Machine
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Preacher Curl Machine Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - One Arm Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - One Arm Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Reverse Barbell Close Grip
Preacher Curl - Reverse Barbell Close Grip
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Reverse Barbell Wide Grip
Preacher Curl - Reverse Barbell Wide Grip
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Barbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Reverse Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Reverse Dumbbell
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Reverse EZ Bar
Preacher Curl - Reverse EZ Bar
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength EZ Bar Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Reverse EZ Bar Wide Grip
Preacher Curl - Reverse EZ Bar Wide Grip
Benefits: Reverse curls work the forearms more than regular bicep curls.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength in both the biceps and the forearms.
Intermediate Forearms Biceps Strength EZ Bar Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps is a straight muscle with two heads. The long head of the biceps crosses both the elbow and the shoulder joints. It bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis muscle, supinates the hand. When the hands are placed in a reverse grip, they work the forearm muscles more.
 Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell Hammer
Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell Hammer
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell Zottman
Preacher Curl - Single Dumbbell Zottman
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. The rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Two Arm Dumbbell
Preacher Curl - Two Arm Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Preacher Curl - Zottman
Preacher Curl - Zottman
Benefits: This exercise isolates the biceps so that momentum does not come into play. the rotation used in this exercise works the forearms.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the biceps.
Beginner Biceps Forearms Shoulders Traps Strength Dumbbell Preacher Bench Pull Gym
General Info: The biceps muscle is a straight muscle with 2 heads. The long head crosses both the elbow and shoulder joints and bends the elbow and raises the arm forward at the shoulder. The short head of the biceps crosses the elbow joint and, in conjunction with the brachioradialis, supinates the hand.
 Press - Floor and Flye Water Bottle
Press - Floor and Flye Water Bottle
Benefits: This exercise works the chest muscles, giving them shape and strength.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Anterior Delts Strength Water Bottle Push Compound Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Press - Floor Reverse and Flye Bottle
Press - Floor Reverse and Flye Bottle
Benefits: This exercise helps to shape and strengthen the chest muscles.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Anterior Delts Strength Water Bottle Push Compound Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Press - Floor Water Bottle
Press - Floor Water Bottle
Benefits: Dumbbells do not limit your movement as much as a barbell does and thus makes greater demands on the stabilizing muscles.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Water Bottle Push Compound Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Press - Floor Water Bottle Inwards
Press - Floor Water Bottle Inwards
Benefits: Dumbbells do not limit your movement as much as a barbell does and thus makes greater demands on the stabilizing muscles.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Water Bottle Push Compound Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Press - Floor Water Bottle Reverse
Press - Floor Water Bottle Reverse
Benefits: Dumbbells do not limit your movement as much as a barbell does and thus makes greater demands on the stabilizing muscles.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Water Bottle Push Compound Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull - Seated Bent Over Water Bottle
Pull - Seated Bent Over Water Bottle
Benefits: This exercise has a different resistance curve from back extensions so these two exercises make a good combination.
Purpose: This exercise can be a powerful tool for developing the spinal erectors.
Intermediate Lower Back Hamstrings Glutes Strength Water Bottle Chair Push Compound Home
General Info: The muscles of the lower back straighten the spine. They work together with the abdominals to keep the spine upright. Good Mornings places a lot of stress on the lower back.
 Pull Down - Close Grip Front Lat
Pull Down - Close Grip Front Lat
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Traps Lats Biceps Posterior Delts Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - Full Range Of Motion
Pull Down - Full Range Of Motion
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Intermediate Lats Traps Biceps Posterior Delts Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - Straight Arm
Pull Down - Straight Arm
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Traps Lats Posterior Delts Strength High Low Cable Machine Pull Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - Underhand Cable
Pull Down - Underhand Cable
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Traps Lats Posterior Delts Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - V Bar
Pull Down - V Bar
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Intermediate Lats Traps Biceps Posterior Delts Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - Wide Grip Behind The Neck
Pull Down - Wide Grip Behind The Neck
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back. To achieve the best effect of this exercise, ensure that your body remains upright.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Lats Biceps Posterior Delts Traps Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Down - Wide Grip Lat
Pull Down - Wide Grip Lat
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Lats Biceps Posterior Delts Traps Strength Lat Pulldown Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull In - Decline
Pull In - Decline
Benefits: This exercise will assist in giving you strong abdominals.
Purpose: This exercise provides flexibility and mobility of the hamstrings.
Beginner Abdominals Hip Flexors Strength Decline Bench Gym
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
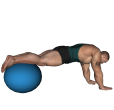 Pull In - Exercise Ball
Pull In - Exercise Ball
Benefits: This exercise will give you a well-defined mid-section.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the abdominal muscles.
Beginner Abdominals Strength Fitness Ball Compound Gym
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
 Pull In - Flat Bench Leg
Pull In - Flat Bench Leg
Benefits: This exercise brings many abdominal muscles into play and trains the deep core muscles.
Purpose: This exercise strengthens the abdominal muscles.
Beginner Abdominals Hip Flexors Hip Extensors Strength Flat Bench Compound Gym Home
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
 Pull In - Seated Flat Bench Leg
Pull In - Seated Flat Bench Leg
Benefits: This exercise will assist in giving you strong abdominals.
Purpose: This exercise provides flexibility and mobility of the hamstrings.
Beginner Abdominals Hip Flexors Strength Flat Bench Gym Home
General Info: The abs can be divided into the abdominals themselves and the obliques. The obliques are the outer abs and are used in twisting movements. For the sake of exercising, the abdominals are sometimes divided into upper abs and lower abs (this is not a technical division but something for exercising). Both upper and lower abs are used in straight line ab exercises while the upper abs are also involved in twisting movements.
 Pull Over - Bent Arm Barbell
Pull Over - Bent Arm Barbell
Benefits: This exercise is an alternative isolation exercise for the development of the lats. It also stretches the pecs.
Purpose: This exercise puts more emphasis on your lats.
Intermediate Lats Shoulders Chest Strength Barbell Flat Bench Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The lats is the larger, flat, dorso-lateral muscle on the trunk, posterior to the arm, and partly covered by the traps on its median dorsal region. It pulls the arm back and down towards the spine.
 Pull Over - Bent Arm Dumbbell
Pull Over - Bent Arm Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise is an alternative isolation exercise for the development of the lats. It also provides an excellent stretch of the pecs.
Purpose: This exercise puts more emphasis on your lats.
Intermediate Lats Shoulders Chest Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Push Compound Gym
General Info: The lats is the larger, flat, dorso-lateral muscle on the trunk, posterior to the arm, and partly covered by the traps on its median dorsal region. It pulls the arm back and down towards the spine.
 Pull Over - Front Raise
Pull Over - Front Raise
Benefits: A barbell allows someone to lift heavier weights and thus build more strength quicker.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Flat Bench Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull Over - Incline and Dumbbell Flye
Pull Over - Incline and Dumbbell Flye
Benefits: This exercise isolates the section of the pecs along the sternum. It also stretches the pecs.
Purpose: This exercise the action of the pecs pulling across the chest, especially focused on the upper pecs.
Beginner Chest Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Push Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull Over - Incline Plate
Pull Over - Incline Plate
Benefits: A barbell allows someone to lift heavier weights and thus build more strength quicker.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Plate Incline Bench Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull Over - Incline Reverse Dumbbell Alternate
Pull Over - Incline Reverse Dumbbell Alternate
Benefits: A barbell allows someone to lift heavier weights and thus build more strength quicker.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull Over - Incline Two Handed Dumbbell
Pull Over - Incline Two Handed Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise is an alternative isolation exercise for the development of the lats.
Purpose: This exercise puts more emphasis on your lats.
Intermediate Lats Shoulders Chest Strength Dumbbell Incline Bench Push Compound Gym
General Info: The lats is the larger, flat, dorso-lateral muscle on the trunk, posterior to the arm, and partly covered by the traps on its median dorsal region. It pulls the arm back and down towards the spine.
 Pull Over - Straight Arm Dumbbell
Pull Over - Straight Arm Dumbbell
Benefits: This exercise is an alternative isolation exercise for the development of the lats. It also stretches the pecs.
Purpose: This exercise puts more emphasis on your lats.
Intermediate Lats Shoulders Chest Strength Dumbbell Flat Bench Push Compound Gym
General Info: The lats is the larger, flat, dorso-lateral muscle on the trunk, posterior to the arm, and partly covered by the traps on its median dorsal region. It pulls the arm back and down towards the spine.
 Pull Over - Wide Grip Decline Barbell
Pull Over - Wide Grip Decline Barbell
Benefits: A barbell allows someone to lift heavier weights and thus build more strength quicker.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and strength speed, and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Decline Bench Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Pull Through - Basic
Pull Through - Basic
Benefits: This is a good exercise for core glute muscle development.
Purpose: This exercise is a controlled, balanced glute exercise for building tone and shape.
Beginner Glutes Lower Back Strength Cable Machine Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The glutes consist of the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. They create hip joint motion to lift the thigh forward, lift the thigh to the side, rotate the leg inward, and rotate the thigh outward.
 Pull Through - Sled
Pull Through - Sled
Benefits: This is a good exercise for core glute muscle development.
Purpose: This exercise is a controlled, balanced glute exercise for building tone and shape.
Intermediate Glutes Lower Back Hamstrings Calves Quads Strength Sled Pull Compound Gym
General Info: The glutes consist of the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. They create hip joint motion to lift the thigh forward, lift the thigh to the side, rotate the leg inward, and rotate the thigh outward.
 Pull Up - Basic
Pull Up - Basic
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building width of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing the width in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and some traps.
Beginner Lats Biceps Traps Strength Chinning Bar Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Up - Rocky Pull Down
Pull Up - Rocky Pull Down
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building width of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing the width in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and some traps.
Beginner Lats Biceps Traps Shoulders Strength Chinning Bar Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Up - V Bar
Pull Up - V Bar
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building width of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing the width in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and some traps.
Beginner Lats Biceps Traps Strength Chinning Bar V-Bar Handle Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Pull Up - Wide Grip Rear
Pull Up - Wide Grip Rear
Benefits: This exercise is a strong, effective free weight back exercise for building muscle mass and size of the lats and middle back.
Purpose: This is a good exercise for increasing strength and size in the upper back. It also involves the biceps and the posterior delts.
Beginner Lats Biceps Traps Strength Chinning Bar Pull Compound Gym
General Info: There are a number of muscles in the back, although the two major muscles are the lats and traps. The lats pulls the arm back and down towards the spine. The traps pull the shoulder blades back and towards the spine.
 Push Up - Bar
Push Up - Bar
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar Close Grip
Push Up - Bar Close Grip
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Triceps Chest Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Bar Hand Stand
Push Up - Bar Hand Stand
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar Hand Stand Wide Grip
Push Up - Bar Hand Stand Wide Grip
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar Leg Raised
Push Up - Bar Leg Raised
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar Leg Raised Close Grip
Push Up - Bar Leg Raised Close Grip
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Triceps Chest Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Bar Leg Raised Wide Grip
Push Up - Bar Leg Raised Wide Grip
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar One Handed
Push Up - Bar One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Bar Wide Grip
Push Up - Bar Wide Grip
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Barbell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Basic
Push Up - Basic
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Close Hand
Push Up - Close Hand
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Triceps Chest Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Feet Elevated
Push Up - Feet Elevated
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise. Elevating the feet makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Flat Bench Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Feet Elevated Close Grip
Push Up - Feet Elevated Close Grip
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Triceps Chest Strength Flat Bench Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Feet Elevated Wide Grip
Push Up - Feet Elevated Wide Grip
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Flat Bench Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Feet On Ball Close Grip
Push Up - Feet On Ball Close Grip
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Triceps Chest Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Feet On Ball Wide Grip
Push Up - Feet On Ball Wide Grip
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Feet On Fitness Ball
Push Up - Feet On Fitness Ball
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise. Elevating the feet makes the exercise more difficult.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Fitness Ball
Push Up - Fitness Ball
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Fitness Ball One Handed
Push Up - Fitness Ball One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Fitness Ball Wall
Push Up - Fitness Ball Wall
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Fitness Ball Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Hand Stand
Push Up - Hand Stand
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise. This is probably the most difficult of all pushup exercises.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Kettlebell Plyo
Push Up - Kettlebell Plyo
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise. The difficulty in this exercise is to switch hands between repetitions.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Chest Triceps Kettlebell Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Leg Raised Clap
Push Up - Leg Raised Clap
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - One Hand
Push Up - One Hand
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - One Handed Bench
Push Up - One Handed Bench
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Flat Bench Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - One Handed Foot Elevated
Push Up - One Handed Foot Elevated
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Chest Triceps Strength Flat Bench Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith High Bar Reverse One Handed
Push Up - Smith High Bar Reverse One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith Low Bar Reverse One Handed
Push Up - Smith Low Bar Reverse One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith Machine High Bar One Handed
Push Up - Smith Machine High Bar One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith Machine Low Bar One Handed
Push Up - Smith Machine Low Bar One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith Machine Mid Bar One Handed
Push Up - Smith Machine Mid Bar One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Intermediate Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Smith Mid Bar Reverse One Handed
Push Up - Smith Mid Bar Reverse One Handed
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Chest Triceps Strength Smith Machine Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
 Push Up - Triceps
Push Up - Triceps
Benefits: Close grip pushups work the triceps more than the chest.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Triceps Chest Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: Typically pushups are considered to be a chest exercise. However, when the hands are placed in a close grip, it works the triceps muscles more. The closer the grip, the more the triceps are worked.
 Push Up - Wall
Push Up - Wall
Benefits: Pushups are a basic body weight chest exercise.
Purpose: This exercise increases strength and produces greater functional strength for pressing movements.
Beginner Chest Triceps Strength Body Only Push Compound Gym Home
General Info: The chest is composed of the Pectoralis Major and the Pectoralis Minor. The Pec Major attaches to the upper arm and pulls the upper arm across the chest. The Pec Minor lies mostly underneath the Pec Major and draws the shoulder blade down and forward.
Could not find your favorite exercise in the list? Please start a discussion and post the name and the list of steps. We will try to add it as soon as we can.